In this article, we will provide you with an overview of Islamic profit-sharing contracts. There are 2 types of profit-sharing contracts which are Mudharabah and Musyarakah. These two contracts are commonly used in financing and deposits products.
The definition of Mudharabah and Musyarakah contracts
Let us first understand what is Mudharabah and Musyarakah. Then only we will appreciate the application of these contracts in Islamic financial products.
Mudharabah
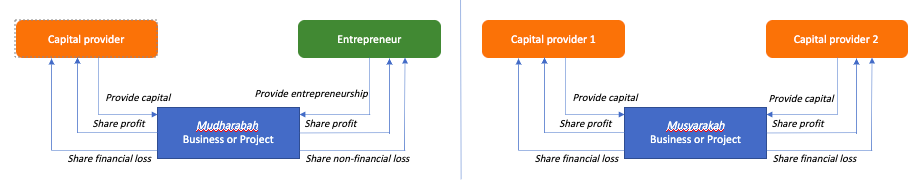
Mudharabah is a contract where the capital provider (known as rabbul mal), provides capital to the entrepreneur (known as mudarib) who contributes his or her skills in a business. Under this arrangement, the capital provider and the entrepreneur share the profits generated from the business. The profit-sharing allocation between the capital provider and entrepreneur is determined and agreed upon at the contract inception.
However, if there is any loss arising from the business, the capital provider will absorb the financial loss in full. An exception applies if such loss arising from the negligence or misconduct of the entrepreneur. Although the entrepreneur did not share the financial loss from the business, he or she suffers a non-monetary loss, specifically the loss of time, and effort in managing the business.
Musyarakah
Musyarakah is an Islamic contract where two or more parties contributes capital to the business. Because all the parties to the arrangement contribute capital to the business, the partners will share any profit or loss arising from the business or arrangement.
The profit-sharing is based on the agreed allocation between the partners as determined at the contract inception. On the other hand, partners share any loss based on the proportion of their capital contributions.
Mudharabah and Musyarakah supports the spirit of risk and rewards sharing between the parties to the arrangement. This is because both parties assumed both risks and rewards from such a partnership.
The application of Mudharabah and Musyarakah contracts in Islamic Finance
Now, let’s see the application of Mudharabah and Musyarakah in Islamic financial products.
Islamic investment account
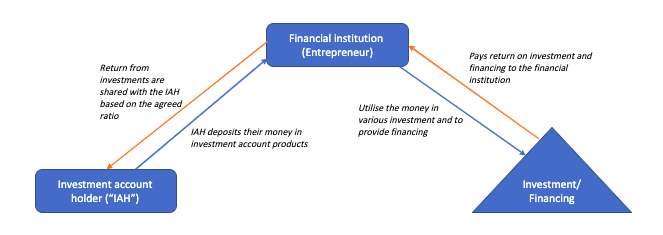
One of the famous Mudharabah and Musyarakah products is the investment account. This product allows depositors to deposit their monies into the investment account. The depositors are known as investment account holders (“IAH”). The financial institutions as the entrepreneurs will then invest the monies deposited by IAH. Financial institutions will use IAH funds to either provide financing to customers or to invest in certain instruments such as government bonds and others.
Any return from the investment or financing will subsequently be shared between the financial institutions and IAH. Because of the risk associated with the investment, the return from the investment account is generally higher than the normal deposit accounts such as Wa’diah (safe-keeping) saving account.
Financing products
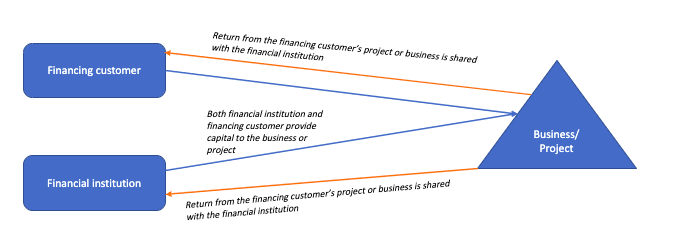
A financial institution may also provide Mudharabah or Musyarakah financing to customers to finance their projects or business. In such a financing arrangement, the financial institution as the capital provider exposes itself to the risk of losing its money from the financing project of the customer.
What is the main issue surrounding the application of Mudharabah and Musyarakah contracts in Islamic Finance?
We explained earlier that in Mudharabah or Musyarakah contracts, the capital provider(s) will need to absorb the financial loss arising from the arrangement. The risks and rewards from Mudharabah and Musyarakah contracts are very much depending on the underlying assets in the arrangement.
Logically, average customers do not put their monies with financial institutions with the expectation to lose them. In fact, there is also expectation that there must always be some returns to customers on deposits with the financial institution. However, the investment account under Mudarabah and Musyarakah do not behave like a normal deposit account. In a normal deposit arrangement, financial institutions have the responsibility to guarantee the principal because the monies are under a safe-keeping arrangement.
Similarly, financial institutions as the capital provider in the Musyarakah arrangement would not want to lose money, which mainly from the customers’ deposits just to lose them in the business or project. Depositors may get the hit from such loss as financial institutions will be lowering the return on deposits.
The financial institutions actively managing this risk through their internal processes. For instance, financial institutions perform a thorough checking and study on feasibility of the proposed business or investments before they invest or extend financing to customers. This is in fact, is the strongest fundamental process in the operation of a financial institution. Accordingly, although there is a risk of losing monies, this risk is very much controlled and minimised in the current environment.

